Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman’s presentation of the sixth Budget on February 1, touted as an interim budget ahead of general elections, aimed to address critical issues such as youth and women empowerment while emphasizing fiscal consolidation and continued capital expenditure. Despite the optimistic outlook presented by the government, a thorough analysis of the promises made versus the economic realities reveals a substantial gap that warrants in-depth scrutiny.
Fiscal Deficit Target vs. Ground Realities:
The Finance Minister’s commitment to lowering the fiscal deficit target for FY25 to 5.1% of
GDP reflects a proactive approach to economic management. However, the ground reality is far
from the promised fiscal prudence, with persistently high food inflation at 9.5% in December 2023.
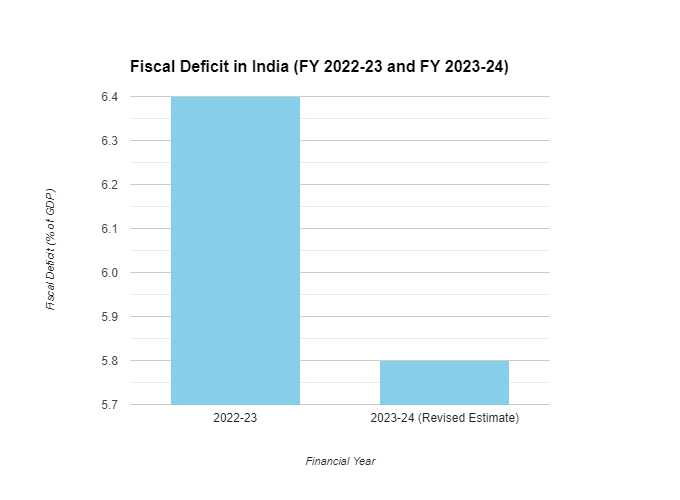
The image shows the Financial Year 2022-23 (April 1, 2022 – March 31, 2023): The actual fiscal deficit was 6.4% of GDP. This was higher than the initial target of 6.7% revised to 6.4% later.
For Financial Year 2023-24 (April 1, 2023 – March 31, 2024): As of today, February 2nd, 2024,
we only have data for the first half of the year. The Revised Estimate for the entire year is 5.8%
of GDP, which is slightly lower than the initial target of 5.9%. However, the final figure may still
change depending on government spending and revenue in the remaining months. Despite the
figures, the Finance Minister commits to lowering the FD to 5.1%.
A detailed examination of the components contributing to the fiscal deficit and inflation would
shed light on the specific areas where the government’s economic policies may need
recalibration. Addressing the root causes of inflation, especially in the food sector, should be a
priority for ensuring sustained economic stability.
'Disha Nirdashak' Baatein vs. Rising Concerns:
Finance Minister Sitharaman’s emphasis on five key principles – social justice, focus on the poor, youth, women, farmers, infrastructure development, and technology utilization – sets the tone for an inclusive and progressive economic agenda. However, the Kantar India Union Budget Survey 2024 reveals rising concerns among Indians about inflation (57%) and job security. This reflects the economic challenges faced by the public, suggesting a disconnection between government assurances and public experiences.

Delving into the specific areas of concern highlighted in the survey, such as inflation and job security, would provide insights into the challenges faced by different segments of the population. Analyzing demographic-specific data could aid in tailoring policies that directly address the needs and aspirations of various groups,
aligning government initiatives more closely with public expectations.
While the government’s commitment to social justice and inclusive governance is commendable, the reality on the ground demands a closer examination of policy implementation. It is crucial to bridge the gap between promises and outcomes by adopting a more nuanced and targeted approach to address the specific challenges faced by different sections of society.
GDP Growth Claims vs Actual Performance
The claim of three consecutive years of 7% GDP growth and being the fastest-growing economy in the G20 appears incongruent with rising inflation and a four-month high in retail inflation at 5.69% in December 2023. Analyzing the components of GDP growth and their impact on inflation would provide a comprehensive understanding of the economic dynamics at play.
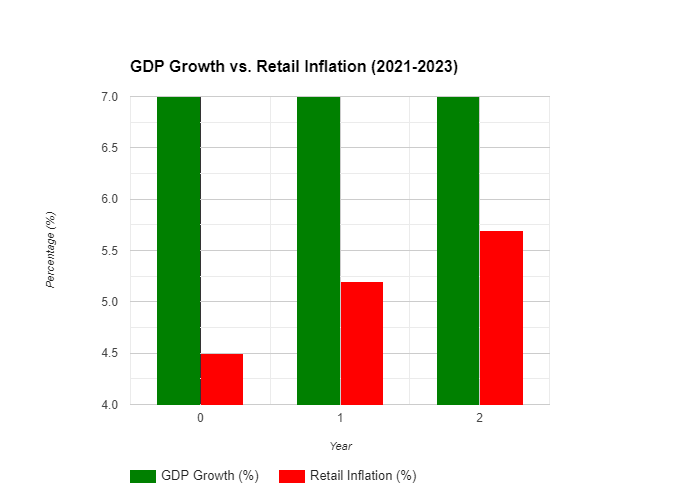
Graph shows no major growth in GDP, however the inflation rates are rising rapidly.
A breakdown of GDP growth by sectors – such as agriculture, manufacturing, and services – could reveal the areas driving economic expansion and those contributing to inflationary pressures. Addressing the specific challenges within each sector would enable the government to formulate targeted interventions that promote sustainable growth without compromising on price stability. Additionally, exploring the global economic context and its impact on India’s growth trajectory can provide valuable insights. Understanding how external factors influence domestic economic performance is crucial for crafting resilient policies that can withstand global uncertainties.
Capex Commitment vs. Household Savings Depletion:
While the government commits to continuing capital expenditure (Capex), Indian households’ gross savings hit a 23-year low at 5.1% of GDP in FY 2022-23. Examining the components of capital expenditure and their link to household savings can offer insights into the factors contributing to this concerning trend. Analyzing the sectors receiving the highest allocations in capital expenditure and their impact on employment and income generation would provide a clearer understanding of the link between government spending and household savings. It is essential to assess whether the current capital expenditure is effectively contributing to economic growth and job creation. Additionally, exploring the role of financial literacy and education in promoting household savings could highlight areas where policy interventions can empower individuals to make informed financial decisions. Bridging the gap between capital expenditure commitments and household savings requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both macroeconomic policies and individual financial empowerment.
IMEC Project vs. Ground Realities:
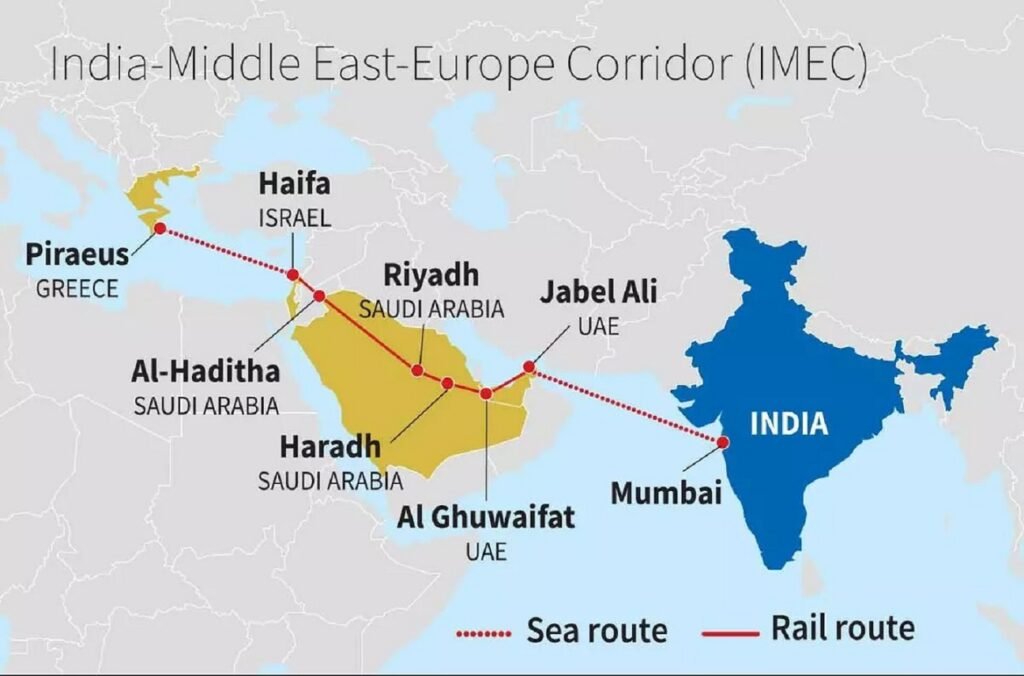
Navigating the Future: The IMEC Project’s Path Through Geopolitical Seas
The commitment to move forward with the India, Middle East, European Corridor (IMEC) project amid disturbances in the Red Sea raises questions about the feasibility and economic impact of such ventures. Analyzing the challenges and opportunities associated with the IMEC project would provide valuable insights into its potential contribution to India’s economic growth.
Delving into the geopolitical and economic factors affecting the progress of the IMEC project can inform a more nuanced assessment of its viability. Evaluating the potential benefits for India in terms of trade, infrastructure development, and geopolitical positioning would contribute to a more informed public discourse on the government’s strategic initiatives.
Furthermore, understanding the potential risks and mitigating measures associated with the IMEC project is essential for ensuring its successful implementation. Transparency in communicating the challenges and opportunities of such ambitious projects is crucial for building public trust and support.
Tax Policies vs. LPG Price Hike:
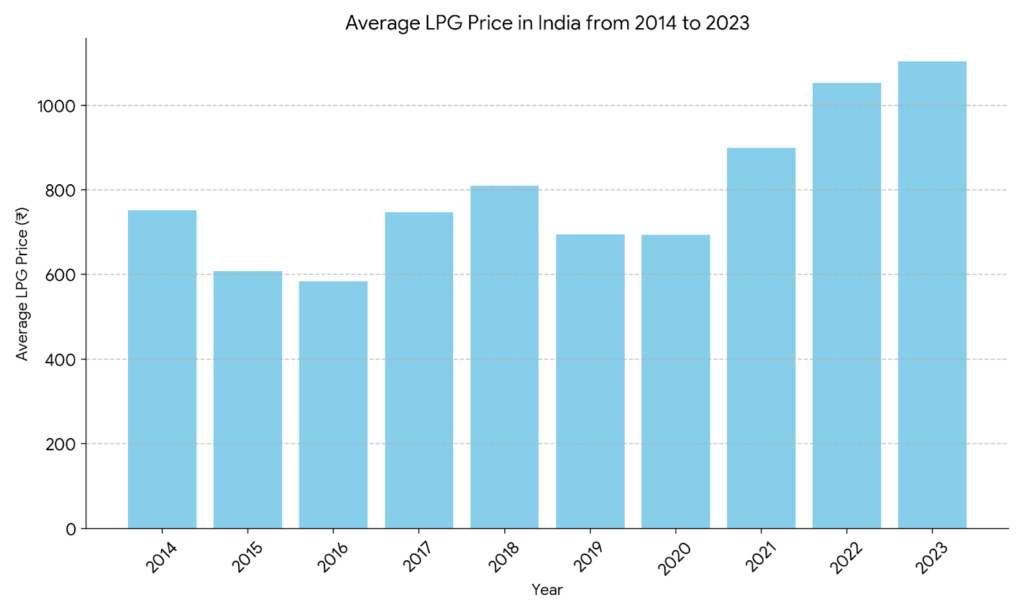
LPG Price Hike since 2014-2023.
Despite no changes in direct and indirect tax rates, the significant increase in non-subsidized LPG cylinder prices by 22% from June 2014 to March 2023 contradicts the promise of stable economic policies. Analyzing the factors contributing to the LPG price hike and their link to tax policies would provide insights into the complexities of energy pricing in the Indian context.
Examining the role of international crude oil prices, domestic taxation policies, and distribution mechanisms in determining LPG prices can shed light on the intricacies of energy pricing. Evaluating the potential impact of alternative energy sources and technologies on reducing the dependency on LPG can inform long-term energy policy decisions.
Additionally, exploring the social and economic implications of LPG price hikes on different demographic groups, especially vulnerable populations, is crucial for designing targeted policy interventions. Balancing the need for revenue generation with ensuring affordable access to essential commodities requires a delicate policy approach that prioritizes the well-being of citizens.
Conclusion:
The promises made during the post-budget presser and the stark economic realities present a dichotomy that cannot be ignored. The government’s commitment to fiscal consolidation, infrastructure development, and addressing social issues seems to be struggling to translate into tangible improvements in the lives of ordinary citizens. As the nation approaches general elections, the juxtaposition of promises and realities serves as a critical lens through which citizens can assess the effectiveness of economic policies and governance.
To bridge the gap between promise and reality, a holistic and nuanced approach is essential. This involves not only refining macroeconomic policies but also addressing the specific challenges faced by different segments of society. By fostering transparency, encouraging public discourse, and incorporating data-driven insights into policy formulation, the government can build a more resilient and responsive economic framework that aligns with the aspirations of the people. The path to inclusive and sustainable development requires a commitment to continuous evaluation, adaptation, and collaboration between policymakers and the public.
References:
Global Food Inflation vs. Indian Food Inflation Report, Dec 2023
BJP 2014 Election Manifesto, Actual Inflation Data, Dec 2023
Price Data from June 2014 to March 2023, Smriti Irani’s 2011 tweet
Retail Inflation Data Dec 2023, RBI’s Tolerance Range
World Bank Data, GDP Implicit Deflator Increase, 2023
Fuel Inflation Data, Excise Duty Hike Impact, 2023
Household Savings Data FY 2022-23
RBI Consumer Confidence Survey, 2023
Kantar India Union Budget Survey 2024
FM live speech on Interim Budget 2024